Per-user Concurrency Limiting
The following policy is based on the Concurrency Limiting blueprint.
Overview
Concurrency limiting is a critical strategy for managing the load on an API. By setting limits on the number of concurrent requests API consumers can make, concurrency limiting ensures balanced resource utilization, preventing a single user or small groups of users from monopolizing resources, which can lead to overloading the API. This approach is key to maintaining service reliability and fair access for all API consumers.
Aperture enforces per-key concurrency limits, offering precise control over API usage. Each unique key is assigned a maximum concurrency limit, which dictates the maximum number of concurrent requests allowed. When this limit is reached new requests are rejected.
The diagram shows how the Aperture SDK interacts with Aperture Cloud to determine whether to allow or reject incoming requests based on the defined maximum concurrency parameters.
Before exploring Aperture's concurrency limiting capabilities, make sure that you have signed up to Aperture Cloud and set up an organization. For more information on how to sign up, follow our step-by-step guide.
Concurrency Limiting with Aperture SDK
The first step to using the Aperture SDK is to import and set up Aperture Client:
- TypeScript
You can obtain your organization address and API Key within the Aperture Cloud
UI by clicking the Aperture tab in the sidebar menu.
The next step is making a startFlow call to Aperture. For this call, it is
important to specify the control point (concurrency-limiting-feature in our
example) and the labels that will align with the concurrency limiting policy,
which we will create in Aperture Cloud in one of the next steps.
- TypeScript
Now, the next part is assessing whether a request is permissible or not by
checking the decision returned by the ShouldRun call. Developers can leverage
this decision to either reject requests made by abusive users or to allow
requests if the concurrent limit has not been crossed. While our current example
only logs the request, in real-world applications, you can execute relevant
business logic when a request is allowed. It is important to make the end call
made after processing each request, in order to send telemetry data that would
provide granular visibility for each flow.
- TypeScript
Create a Concurrency Limiting Policy
- Aperture Cloud UI
- aperturectl
Navigate to the Policies tab on the sidebar menu, and select Create Policy
in the upper-right corner. Next, choose the Rate Limiting blueprint, select
Concurrency and complete the form with these specific values:
Policy name: Unique for each policy, this field can be used to define policies tailored for different use cases. Set the policy name toconcurrency-limit-test.Max concurrency: Configures the maximum number of concurrent requests allowed. SetMax concurrencyto20.Limit by label key: Determines the specific label key used for enforcing concurrency limits. We'll useuser_idas an example.Max inflight duration: Configures the time duration after which a flow is assumed to have ended in case end call is missed. SetMax inflight durationto60s.Control point: It can be a particular feature or execution block within a service. We'll useconcurrency-limiting-featureas an example.
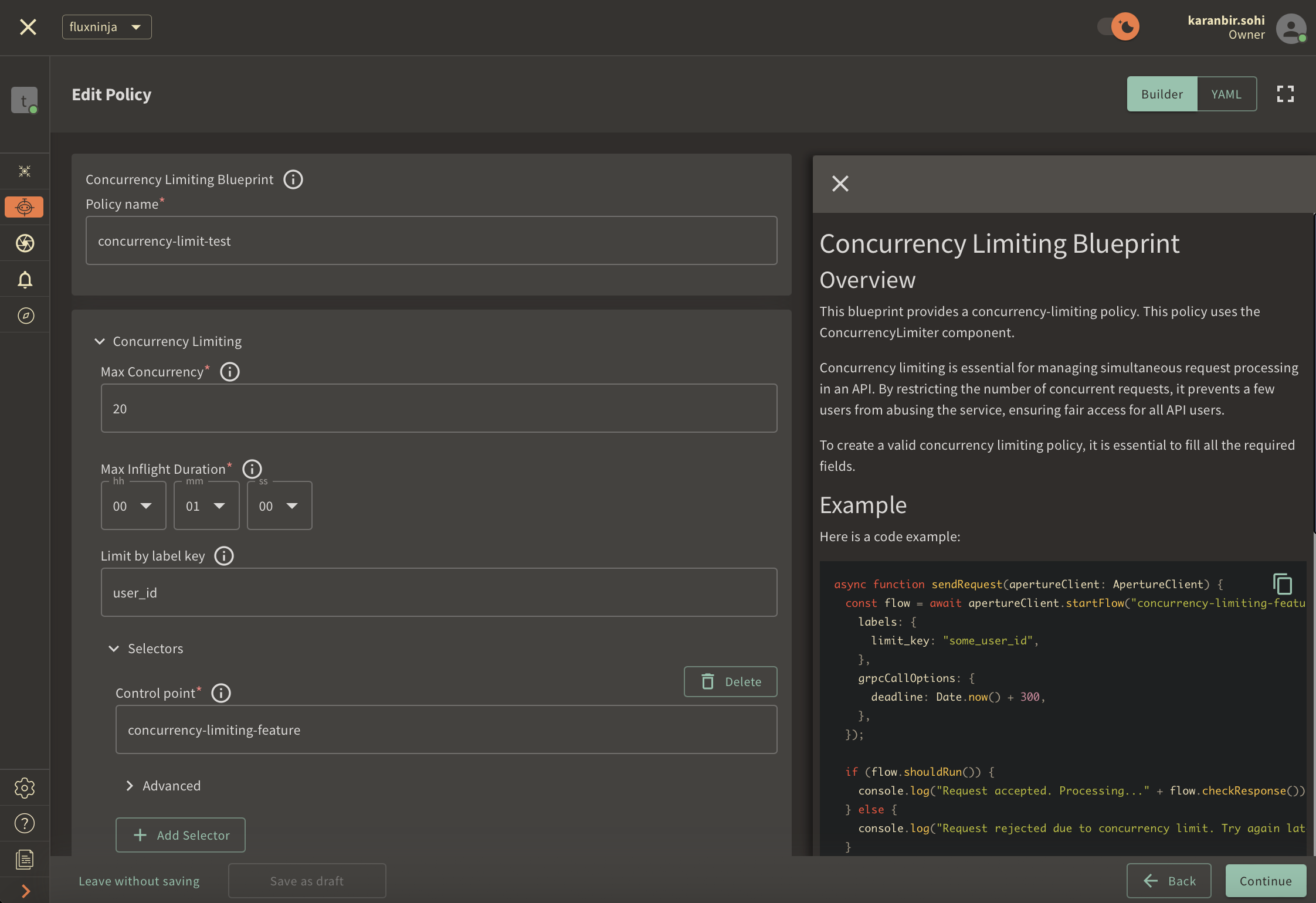
Once you've entered these six fields, click Continue and then Apply Policy
to finalize the policy setup.
If you haven't installed aperturectl yet, begin by following the Set up CLI aperturectl guide. Once aperturectl is installed, generate the values file necessary for creating the concurrency limiting policy using the command below:
aperturectl blueprints values --name=concurrency-limiting/base --output-file=concurrency-limit-test.yaml
Following are the fields that need to be filled for creating a concurrency limiting policy:
policy_name: Unique for each policy, this field can be used to define policies tailored for different use cases. Set the policy name toconcurrency-limit-test.max_concurrency: Configures the maximum number of concurrent requests allowed. Setmax_concurrencyto20.limit_by_label_key: Determines the specific label key used for enforcing concurrency limits. We'll useuser_idas an example.max_inflight_duration: Configures the time duration after which a flow is assumed to have ended in case end call is missed. Setmax_inflight_durationto60s.control_point: It can be a particular feature or execution block within a service. We'll useconcurrency-limiting-featureas an example.
Here is how the complete values file would look:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=../../../../../blueprints/concurrency-limiting/base/gen/definitions.json
blueprint: concurrency-limiting/base
uri: ../../../../../blueprints
policy:
components: []
policy_name: concurrency-limit-test
resources:
flow_control:
classifiers: []
concurrency_limiter:
alerter:
alert_name: "Too many inflight requests"
max_concurrency: 20
parameters:
limit_by_label_key: "user_id"
max_inflight_duration: 60s
request_parameters: {}
selectors:
- control_point: concurrency-limiting-feature
The last step is to apply the policy using the following command:
aperturectl cloud blueprints apply --values-file=concurrency-limit-test.yaml
For this policy, users are permitted to make up to 10 concurrent requests in before hitting the concurrency limit. Additional requests made after the maximum number of concurrent requests is reached are rejected.
Next, we'll proceed to run an example to observe the newly implemented policy in action.
Concurrency Limiting in Action
Begin by cloning the Aperture JS SDK.
Switch to the example directory and follow these steps to run the example:
- Install the necessary packages:
- Run
npm installto install the base dependencies. - Run
npm install @fluxninja/aperture-jsto install the Aperture SDK.
- Run
- Run
npx tscto compile the TypeScript example. - Run
node dist/concurrency_limit_example.jsto start the compiled example.
Once the example is running, it will prompt you for your Organization address and API Key. In the Aperture Cloud UI, select the Aperture tab from the sidebar menu. Copy and enter both your Organization address and API Key to establish a connection between the SDK and Aperture Cloud.
Monitoring Concurrency Limiting Policy
After running the example for a few minutes, you can review the telemetry data
in the Aperture Cloud UI. Navigate to the Aperture Cloud UI, and click the
Policies tab located in the sidebar menu. Then, select the
concurrency-limiter-test policy that you previously created.
Once you've clicked on the policy, you will see the following dashboard:
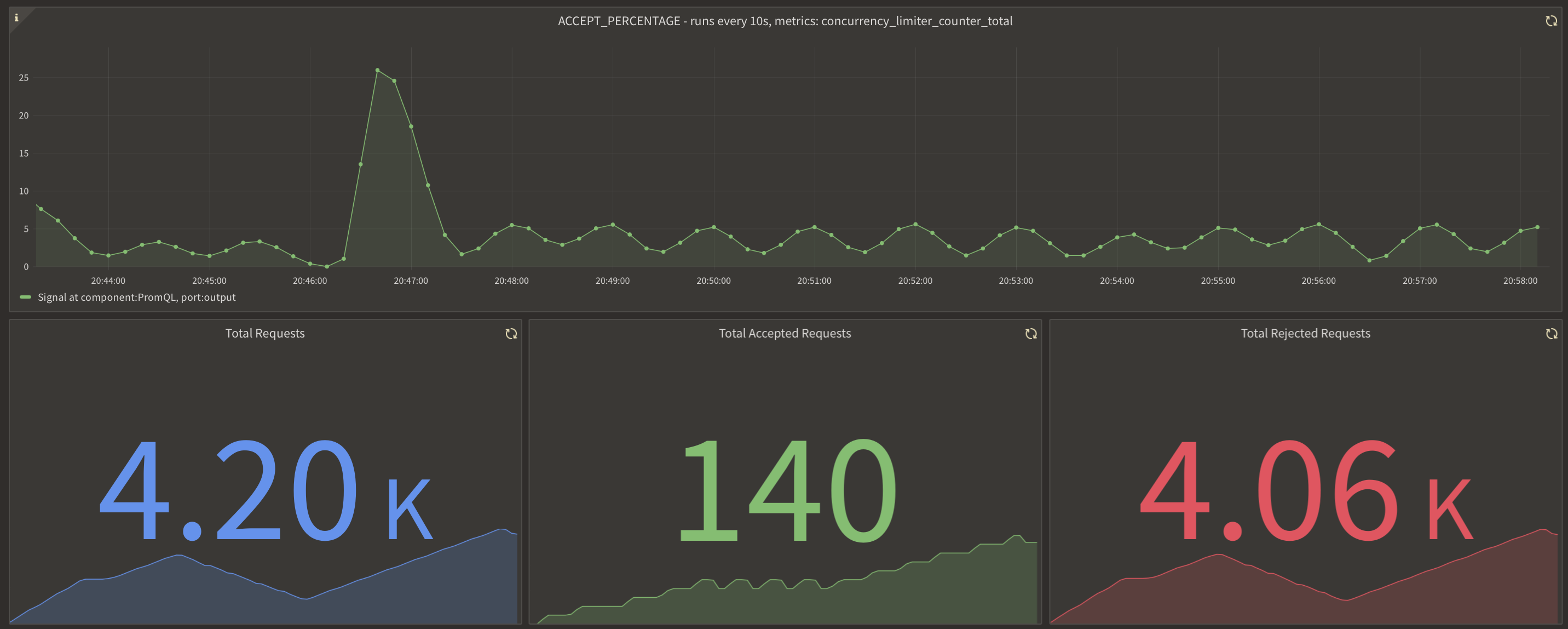
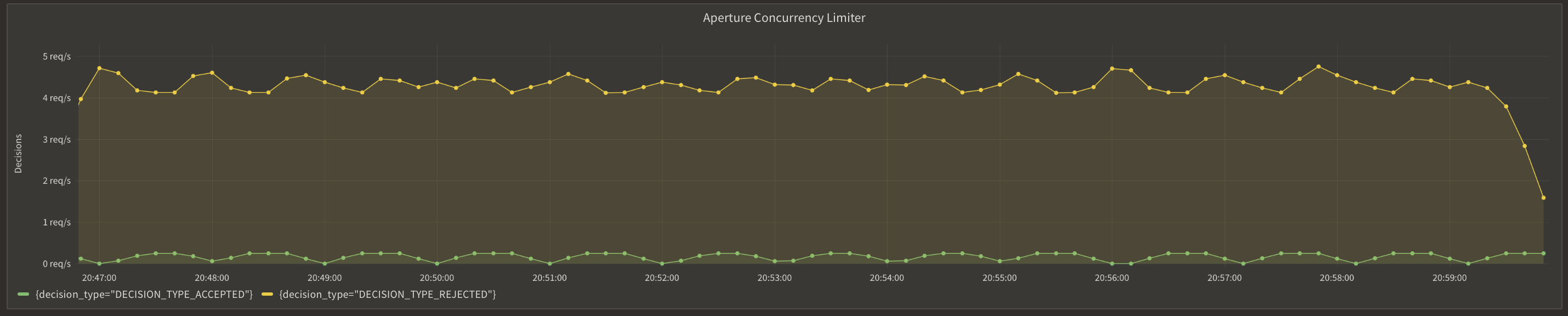
These panels provide insights into how the policy is performing by monitoring the number of total, accepted and rejected requests along with the acceptance percentage. Observing these graphs will help you understand the effectiveness of your concurrency limiting setup and help in making any necessary adjustments or optimizations.